¿Qué es la carga V2G?
V2G son las siglas de Vehicle-to-Grid, que describen un novedoso sistema energético que utiliza puertos de carga bidireccionales conectados a los hogares. Estos puertos conectan los vehículos eléctricos de batería (BEV) o los vehículos eléctricos híbridos enchufables (PHEV) a la red, lo que permite a estos vehículos eléctricos no solo extraer energía de la red, sino también devolver a esta la energía sobrante.
V2G cargando se refiere al uso de cargadores bidireccionales de VE (sistemas de conversión de CC a CA) para suministrar energía desde las baterías de los VE a la red. La V2G puede ayudar a equilibrar y satisfacer las necesidades energéticas locales, regionales o nacionales mediante la carga inteligente.
El principio de la carga bidireccional V2G
La idea central del V2G es aprovechar la energía almacenada en las baterías de los vehículos eléctricos cuando no se utilizan y cargarlas o descargarlas según sea necesario. Cuando se cargan, los vehículos eléctricos reciben corriente alterna (CA) de la red, que luego se convierte en corriente continua (CC) (ya sea mediante un convertidor integrado en el vehículo o un cargador externo). Para utilizar la energía almacenada en la batería del VE para alimentar una vivienda o devolverla a la red, la corriente continua del vehículo debe convertirse de nuevo en alterna, tarea que realiza el cargador bidireccional. La carga bidireccional es especialmente eficaz cuando se complementa con energía solar, ya que puede generar energía adicional durante los periodos de luz solar intensa.
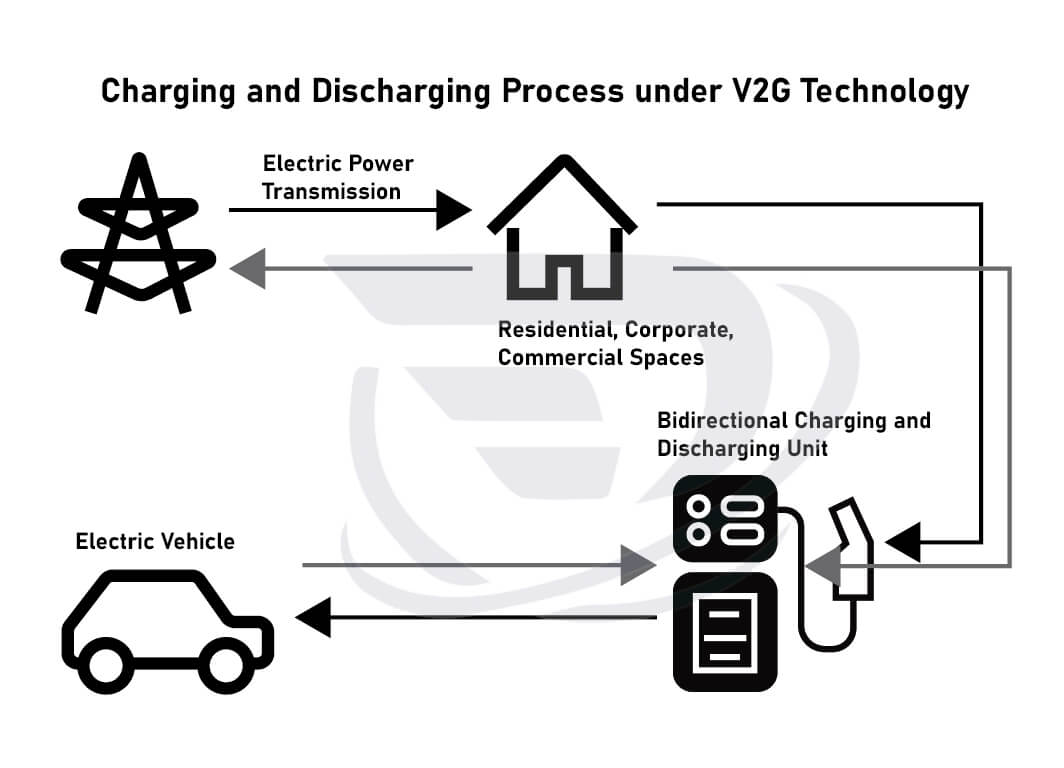
Ventajas de la carga bidireccional V2G
1. Gran capacidad de almacenamiento de energía en las baterías de los VE, capaces de almacenar hasta 10 veces más energía que las típicas baterías de iones de litio de 7 KWH que suelen encontrarse en los sistemas solares fotovoltaicos residenciales.
2. Ahorro de costes y mejora de la eficiencia para los propietarios de vehículos eléctricos mediante recompensas o reducción de los costes energéticos. Cargar los vehículos durante las horas valle a las tarifas más bajas y devolver la energía a la red durante las horas de mayor consumo puede reducir los gastos energéticos totales.
3. Alivia la tensión de la red en periodos de gran demanda, como las olas de calor.
4. Aumenta la eficiencia energética al reducir la dependencia de la red, sobre todo cuando se combina con paneles solares en los tejados. Nuevos modelos de negocio y asociaciones promueven el uso de energías renovables y la venta del exceso de energía a la red.
Desventajas de la carga bidireccional V2G
1. Disponibilidad limitada de cajas murales en el mercado, lo que reduce la competencia en cuanto a precios y opciones.
2. Costes más elevados en comparación con los cargadores estándar para VE.
3. Actualmente es ventajoso sobre todo cuando se carga en casa o se utilizan cargadores específicos en el lugar de trabajo.
4. El uso excesivo de la batería del vehículo puede provocar su envejecimiento prematuro.
5.Siguen sin resolverse los problemas de seguridad.