Als entscheidende Komponente für das Wärmemanagement im Batteriesystem hat die Wasserkühlplatte einen großen Einfluss auf die Sicherheit und Lebensdauer des Batteriesystems.
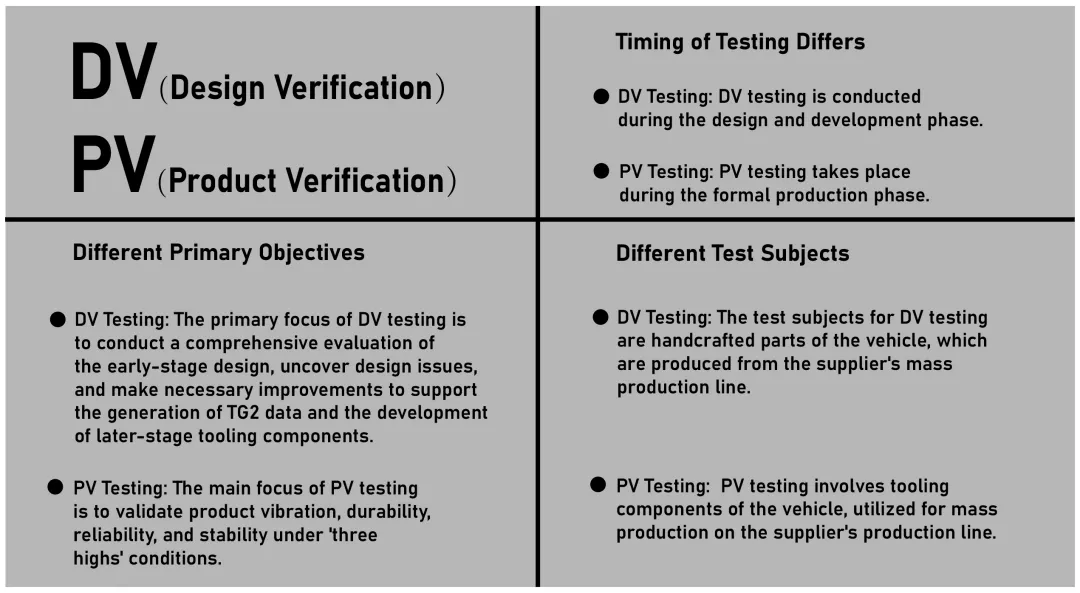
Ja, DV- und PV-Tests sind also unerlässlich, um sicherzustellen, dass Wasserkühlplatten die strengen Normen für das Wärmemanagement erfüllen. Diese Tests bestätigen die Zuverlässigkeit der Konstruktion und die Konsistenz der Produktion und minimieren die Risiken bei der Produktentwicklung.
In der Industrie gab es schon einmal einen größeren Fehler, der auf unsachgemäße Tests während der Entwicklung zurückzuführen war. Stellen Sie sicher, dass robuste Tests Fehler frühzeitig erkennen, damit sie vor der Massenproduktion korrigiert werden können.
Wie kann der DV- und PV-Prüfprozess optimiert werden?
Ein rationalisierter Testprozess verkürzt die Zeit bis zur Markteinführung und gewährleistet, dass die Produkte den Qualitätserwartungen entsprechen. Optimierung ist der Schlüssel zu einer effizienten Projektabwicklung.
Arbeiten Sie mit erfahrenen Anbietern zusammen, die über Testkompetenz verfügen, wie z. B. XD THERMAL. Effizient verwaltete Tests senken die Kosten und beschleunigen die Zeitpläne.
XD THERMAL kann DV- und PV-Tests durchführen
Struktursimulation (Teilansicht)
- 1. Modalanalyse
- 2. Statische/dynamische Steifigkeit der Schraubenbefestigungspunkte
- 3. Zufallsschwingungen GB 38031-2020
- 4. Schwingungsermüdungssimulation GB/T 31486
- 5. Mechanischer Schock ISO 19453-2020
- 6. Ablegen
- 7. Schaben am Boden
- 8. Druckwiderstand der Deckplatte
- 9. Expansionskraft
Thermische Simulation (Teilansicht)
- 1. Druckverlust der Kühlplatte
- 2. Temperaturisolierung Leistung
- 3. Prüfung des Wärmeaustauschs
- 4. Leistung der Wärmedämmung
- 5. Parken Temperatur Isolierung Leistung
- 6. Langsame Aufladung bei niedrigen Temperaturen
- 7. Schnelles Laden bei hoher/niedriger/Raumtemperatur
Produktverifizierungstests (Teilansicht)
- 1. Kühlplatte Leckagetest
- 2. Druckabfallprüfung
- 3. Berstprüfung
- 4. Vakuumtest
- 5. Test bei konstant hoher Temperatur und hoher Luftfeuchtigkeit
- 6. Temperaturwechsel des Kühlmittels
- 7. Mechanischer Schock
- 8. Vibration
- 9. Druckpulsation
- 10. Kühlmittelkompatibilität
- 11. Temperaturschock
- 12. HIPOT-Test
- 13. Maßkontrolle
- 14. Innere technische Sauberkeit
Ein erfahrener Anbieter verfügt über eine gut eingeführte Standardarbeitsanweisung (SOP) für DV- und PV-Prüfungen sowie über hochmoderne Einrichtungen. Er sollte End-to-End-Dienstleistungen anbieten, von der Designunterstützung bis zur Massenproduktion. Die umfassende Erfahrung von XD THERMAL in internationalen OEM-Projekten und die Fähigkeiten als Full-Service-Lieferant machen uns zu einem idealen Partner für umfassende Prüf- und Produktionsanforderungen.